Blog, Network Cabling, Networking Device
Network Connectors: A Complete Guide (2025)
Connection happens in every corner of the world. In networking, cables are crucial to creating connections. So are network connectors. In simple words, they are a bridge linking one device to another to exchange data and information.
Network cable connectors have various types and work for certain purposes. This article is a complete guide. It will give you an overview of these types and describe how they work. Let’s get started!
Table of contents
What is a Network Connector
Whether you link your router or play the latest game online, a network cable connector plays a vital role. This device is either physical or virtual. It ensures that users transfer vast amounts of data from devices, such as computers, to others, like routers.
Network connectors also ensure data transmission across systems in network segments. These include local area networks (LANs), wide area networks (WANs), etc. The media helping to transfer data are network cables and fiber optic cables. The commonly seen Ethernet cable is the RJ45, the full name being “registered jack 45”. We will explain the RJ45 connector in the following section.
Simple home networks use a special network connector (mostly an Ethernet cable) to achieve a connection between computers and routers. In larger networks, network cable connectors should use fiber optics with high-speed transmission.
Types of Network Connectors
Network cable connectors have various types, but they basically fall into four categories.
Physical Network Connectors
RJ45: It is a modular plug used for network cabling. It is not technically correct to call so; instead, its strict name is “8P8C modular plug”. “8P8C” means “8 Positions and 8 Contacts”, which is useful at the end of Ethernet cables.

RJ11: This connector is smaller than RJ45 in its appearance. With 2 or 4 pins, it is used for telephone connections. Please don’t mistake it for the RJ45 connector because of their similar shapes.
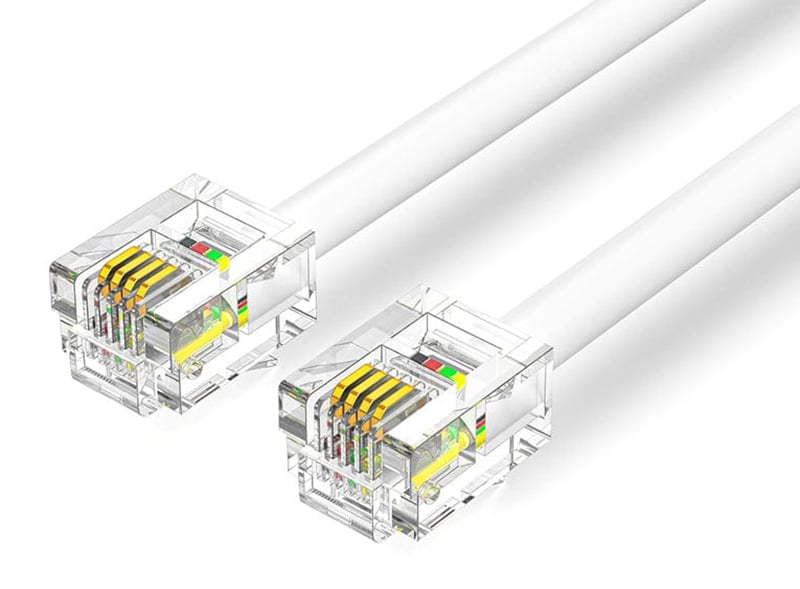
RJ12: It has a similar shape to RJ11, and it is a 6P6C (6-position 6-conductor) module connector. You can use it in telephone systems and some low-speed serial communication devices.

RJ14: It is also for telephone system use, with a similar look as that of RJ11. It uses four wires and is suitable for multiline phones.
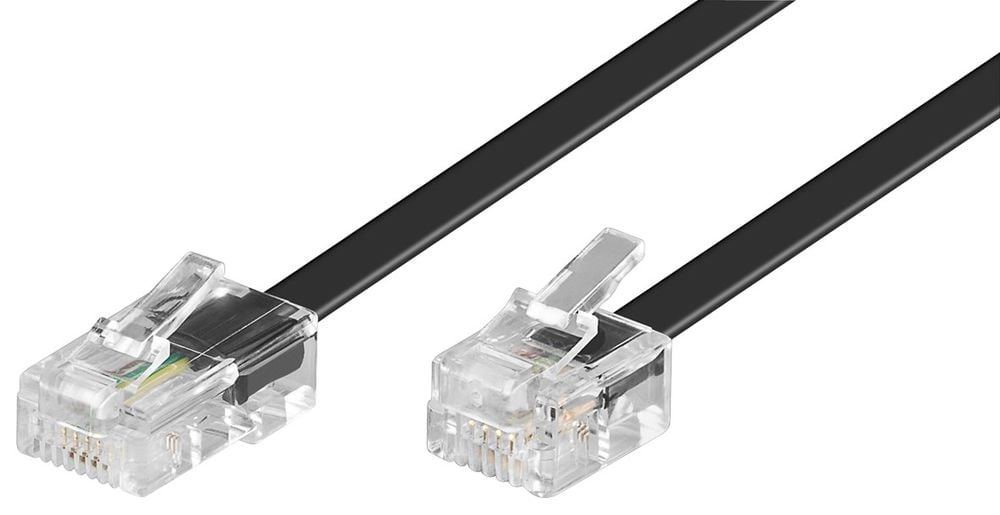
RJ22: It is a 4-position 4-conductor (4P4C) modular connector used for telephone handsets instead of data transmission.

RJ48: With eight contacts, this connector applies to telecommunication and data circuits, especially T1/E1 lines, ISDN, and DSX-1 connections.
.jpg)
RJ50: It has ten positions and ten conductors. Its shape is larger than RJ45, and its usages include data acquisition systems and proprietary serial interfaces.
-933x700.webp)
RJ61: It supports multiple telephone lines and uses T568A (for Europe) and T568B (outside Europe) standards. So, a single cabling standard can be used for data and voice.

M12: This connector applies to harsh industrial conditions. It can transfer data, signals, or even power. You can find it in sensors, automation, and robotics.

Fiber Optic Connectors: They are suitable for fiber-optic networks. Light signals, rather than electrical ones, are used by these connectors to transfer data. The common types are SC, ST, LC, FC, MPO, MTP, and MT-RJ. As a reliable supplier in the networking sector, OPTCORE offers fiber optic patch cables with different lengths.
OPTCORE Fiber Patch Cables
-
SC-SC 40/100GB OM4 Multimode LSZH Duplex Fiber Patch Cable
Price range: US$ 3.70 through US$ 73.00 (Excl. VAT) -
HP QK734A Compatible LC-LC Multi-mode OM4 Duplex Fiber Optic Cable
US$ 9.00 (Excl. VAT) -
MPO Female to 4 LC Duplex Fiber Breakout Cable, 8 Fiber 50/125 Multimode OM3, Type B, LSZH
Price range: US$ 25.00 through US$ 223.00 (Excl. VAT) -
Juniper MTP-4LC-M3M Compatible MTP to 4x LC Duplex Multi-mode OM3 Breakout Fiber Cable
US$ 36.00 (Excl. VAT)
Further Reading
Coaxial Connectors: They achieve cable broadband connections. One type of this is BNC (Bayonet Neil-Concelman), a coaxial radio frequency connector. It is suitable for low-frequency and radio-frequency devices, such as legacy Ethernet systems.
USB: It is a network connector for specific devices, such as USB-to-Ethernet adapters.

Software Network Connectors
They are virtual elements that establish communication between networks. These include VPN connectors and API connectors. The former creates secure connections between remote users and private networks. The latter is crucial in cloud computing, making various systems “communicate” smoothly and allowing platforms to exchange data easily.
Wireless Network Connectors
A wireless router or access point functions as a network connector in wireless networks. It links your devices without wiring to local networks. Bluetooth allows users to connect a range of devices, including headsets and smartphones. Zigbee or Z-Wave has a low power, linking IoT (the Internet of Things) devices.
Special Network Connectors
SFP is short for small form-factor pluggable; these connectors are popular with data centers and enterprises. They fit high-speed fiber optic or copper network connections.
M.2 and Mini PCIe are tiny connectors, and they link network cards or Wi-Fi modules in laptops or embedded systems.

How Network Connectors Work
Network cable connectors are physical or virtual devices, and they enable data transfer. How do they actually work? Let’s start with physical connectors like RJ45 and optical fiber.
Functions of the RJ45 Connectors: You can find them in telephone systems, but they have wider usage in the networking sector. When a device is linked by the RJ45 connector using Ethernet cables, electrical signals transfer data from it to the device at the other end. Then, the connector converts the signals into digital data.
Roles of Fiber Optic Connectors: Unlike Ethernet connectors, fiber optic connectors transmit data in the form of light pulses. These connectors are ideal for high-speed, long-distance networking, transferring data as light signals.
Functions of Other Network Connectors: Wi-Fi network connectors use radio waves to link your laptops to a wireless router. With the help of radio signals, the router makes data transfer and reception possible. Virtual connectors, especially VPN connectors, use encryption protocols to communicate securely with devices via an unsecured public network.
FAQs
How many Ethernet network cables does OPTCORE offer?
Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6A, Cat7, and Cat8 network cables are available. They also come in shielded or unshielded types.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of RJ45 Connectors?
RJ45 connectors are reliable, compatible, simple to use, and affordable. Also, they support high-speed data transmission and a bandwidth of up to 100Mbps. However, they are a little difficult to install. They also suffer physical damage or limit the mobility of connected devices.
What are the three types of Ethernet Connectors?
These connectors link coaxial cables, twisted pair cables, and fiber optic cables. Coaxial cable connectors join coaxial cables to devices, such as the modem, the router, and the TV. The RJ45 connector is the widely used twisted cable connector, linking computers, switches, routers, etc. Fiber optic cable connectors use fiber optic cables for networking device connection.
Conclusion
To sum up, network connectors or network cable connectors are the tools for secure and convenient data transmission. In this complete guide, you can learn how these connectors function. Among their many types, RJ45 and fiber optic connectors are essential to the IT sector. Knowing their functions also helps you choose the correct connector.
Read More:
- Fiber Connector Types: A Complete Guide (2024)
- MTP vs MPO connector: What is the difference?
- RJ45 vs RJ11 vs RJ12 Connector, What is the Difference?
- APC vs UPC vs PC Fiber Connector, What is the Difference?










