Blog, Network Cabling
What is WWAN? An Intro to Wireless WAN
Network connectivity is common in today’s digital world, and many network technologies are thriving. WWAN, or Wireless Wide Area Network, is built on the foundation of WAN, which stands for Wide Area Network. WWAN improves the flexibility and convenience of connecting to the internet through wireless communication. This eliminates the need for wired connections and reduces costs for wiring and equipment. Users can connect to the network anywhere within their cellular provider’s coverage area.
This article will explain WWAN in detail. It will cover how it differs from other network types, its key components, development over time, benefits, limitations, and more. This information will help you understand this important network technology.
Table of contents
What is WAN?
WAN stands for Wide Area Network, which can cover a large geographic area, such as a city, a country, or even the globe, and can be used for long-distance data transfer between different networks. WAN usually connects multiple Local Area Networks (LANs) and other types of networks, allowing computer networks in various locations to communicate and share resources. In contrast, a LAN (local area network) is a computer network that interconnects computers in a limited area.
What is WWAN?
WWAN is a Wireless WAN (Wireless Wide Area Network), a vast area network based on cellular technology. The emergence of WWAN technology has extensively promoted the development of mobile Internet. Users can connect to the WAN network through wired or wireless connections, and WWAN is wireless. It transmits data via wireless signals over a wide geographic area, such as an area or global area, allowing users to access the network without relying on a wired connection.
Typically, laptops, tablets, and some smartphones have integrated WWAN capabilities. As long as you’re in a cellular service area, you can connect to the web, watch Ultra HD video, handle work emails, and more whenever and wherever you want. Standard WWAN technologies include 3G, 4G LTE, emerging 5G networks, and Satellite links.
WWAN Technical Standards:
1. GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications)
GSM is a digital mobile communication technology that provides voice and data services worldwide. It is the basis of WWAN technology and supports data transmission speeds up to 56kbps.
2. CDMA (Code Division Multiple Access)
CDMA is a method of transmitting digital signals simultaneously over the same carrier frequency (channel) and is widely used as a cellular transmission technology. CDMA provides call capacity 5 times faster than GSM systems. Although CDMA and GSM have been the two main cellular networks for many years, they are incompatible with 2G and 3G transmission systems.
3. LTE (Long Term Evolution)
LTE is a 4G mobile communications technology that replaces 3G. It uses GSM’s software infrastructure but with a different hardware interface. Before 4G, voice was handled primarily over traditional circuit-switched networks, which changed with LTE’s Evolved Packet System (EPS), which allows both voice and data to be transmitted in IP packets. LTE is one of the dominant WWAN technologies, supporting data transfer speeds of up to several hundred Mbps.
4. 5G (The Fifth Generation of Cellular Network Technology)
5G is the next generation of mobile communication technology, offering higher data transmission speeds, lower latency, and greater network capacity. Currently, 5G is gradually replacing LTE as the mainstream WWAN technology.
Main Key Components of WWAN
1. Mobile Terminals
Mobile terminals, such as smartphones, tablet PCs, mobile routers, and some IoT devices with wireless WAN access functions, belong to this category. These devices have built-in corresponding wireless communication modules (e.g., 4G module, 5G module), which can establish a wireless link with the base station so that users can realize operations such as browsing on the Internet, sending messages, and making phone calls through network services provided by operators.
2. Base Station
The base station is an essential WWAN network infrastructure for wireless communication with mobile devices. BTS transmits and receives wireless signals to realize data transmission with mobile terminals. For example, in the city, we often see mobile communication base station towers designed to ensure that mobile devices, such as cell phones in the surrounding area, can easily access the WWAN network. The coverage and signal strength of the base station affect the user’s network experience in the area.
3. User Equipment
UE refers to all kinds of mobile terminal devices, such as cell phones, tablet PCs, mobile routers, etc., that access the WWAN network. These devices have built-in WWAN communication modules and can wirelessly communicate with the base station to realize data transmission and reception. The performance of different UE devices in a WWAN network varies.
4. SIM card
The SIM card stores user-related identification information, such as the International Mobile Subscriber Identity (IMSI) and other key data. Once a valid SIM card is inserted into the mobile terminal, the network operator can read the information in the card to authenticate the user and determine whether the user has the right to use the WWAN network services provided by the network operator.
WWAN vs WAN vs WLAN vs WPAN, What is the difference?
WAN vs. WWAN
WAN mainly focuses on wired network connections in large geographical areas. People often build network infrastructure in a WAN network by laying many wired communication lines. WWAN, on the other hand, is based on wireless communication technology to realize wide-area network connectivity without relying on wire cables.
WWAN vs. WLAN
WLAN (Wireless Local Area Network) has a relatively small coverage area. This type of network coverage is usually limited to a building or a small confined area, such as a home, office, or shopping mall. It mainly uses Wi-Fi technology for wireless communication, and the transmission distance is relatively short usually tens or hundreds of meters. WWAN, on the other hand, uses telecom cellular network technologies such as 2G, 3G, 4G LTE, and 5G to transmit data. They can realize a more comprehensive coverage area across cities, regions, and countries.
WWAN vs. WPAN
WPAN (Wireless Personal Area Network) is mainly used for short-distance wireless connection between personal devices, with a coverage range of about 10 meters. It mainly uses Bluetooth technology for wireless communication. WPAN is commonly used to connect cell phones with Bluetooth headsets, smartwatches, etc. The coverage of WWAN is much more extensive than WPAN. Its primary purpose is to realize the connection between mobile devices and wide-area networks rather than the short-distance interaction between personal devices.
Evolution of WWAN
Early stage
The 2G network is an early form of WWAN development. It mainly provides voice calls and simple SMS service, and the data transmission rate is low, generally around tens of kbps. At this stage, mobile devices were mainly feature phones, and people used cell phones more for essential communication. For example, cell phones could only send SMS and browse some simple WAP web pages, and the network application was relatively single.
Development Stage
With the advancement of technology, the emergence of the 3G network significantly improved the data transmission capacity of WWAN, and the data rate could reach several hundred kbps to several Mbps. This made mobile Internet applications emerge, such as cell phones that can smoothly browse graphic and textual web pages, watch low-quality online videos, and use some simple mobile applications. Smartphones also became popular during this period. The ecology of mobile Internet began to form gradually.
Mature stage
The 4G LTE network significantly increases the data transmission rate of WWAN, and the theoretical peak rate can reach hundreds of Mbps or even higher. At this stage, those applications with high bandwidth requirements, such as high-definition video playback and large file downloads, are widely popularized.
Innovation Stage
5G networks, a next-generation technology standard of WWAN, were launched in the early 2020s. They not only have higher transmission rates, with theoretical peak rates of several Gbps but also lower latency and greater connection density. They are the fastest and most reliable WWAN technology to date, with speeds up to 20 times faster than 4G.
Advantages of WWAN
- High mobility: One of WWAN’s most significant advantages is its excellent mobility. Users can access the network anytime and anywhere as long as they are within the coverage area of the WWAN network. For example, a businessman on a business trip can use his laptop to handle work emails and participate in a video conference via WWAN anytime, anywhere.
- Broad coverage: WWAN can realize global wireless coverage, including in cities, villages, and even some remote areas.
- Convenient deployment: Since WWAN is based on wireless communication technology, it does not need to lay wired communication lines on a large scale like WAN, so its deployment is relatively convenient. Network operators can quickly establish base stations and other infrastructure to expand network coverage according to demand.
Disadvantages of WWAN
- Signal affected by the environment: WWAN signals are easily affected by environmental factors in the transmission process, such as building blockage, terrain ups and downs, bad weather, etc. For example, when the user is in the basement or elevator, it is not easy for the user to get the signal. The network connection may be unstable or unable to connect due to the blocked signal.
- Limited network capacity: Although WWAN’s network capacity is increasing with the development of technology, in areas with dense users, such as large shopping malls and concert venues, a large number of users accessing the network at the same time may lead to network congestion and slow speed.
- Higher data transmission cost: Compared with wired networks, WWAN has a relatively high data transmission cost. Users using WWAN for large data transmission, such as watching high-definition videos for a long time, may incur higher costs. For example, some traffic packages require users to pay extra fees after exceeding the package limit and limiting the amount of usage.
- Lower security: Since data is transmitted wirelessly, WWANs may be vulnerable to security wireless communication risks like other wireless technologies.
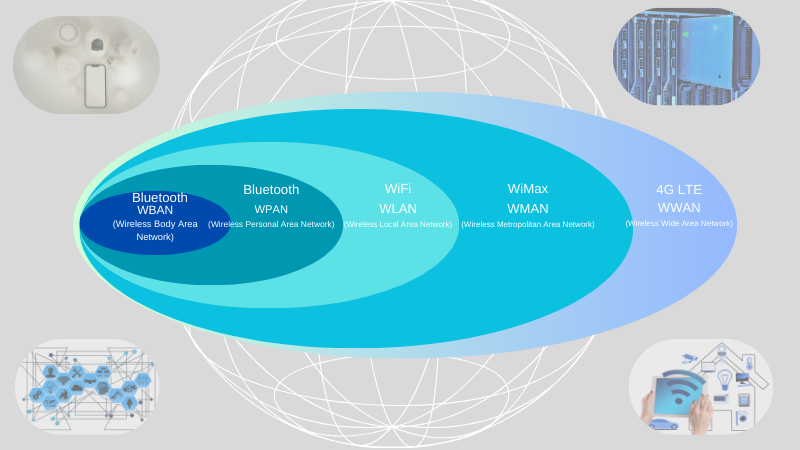
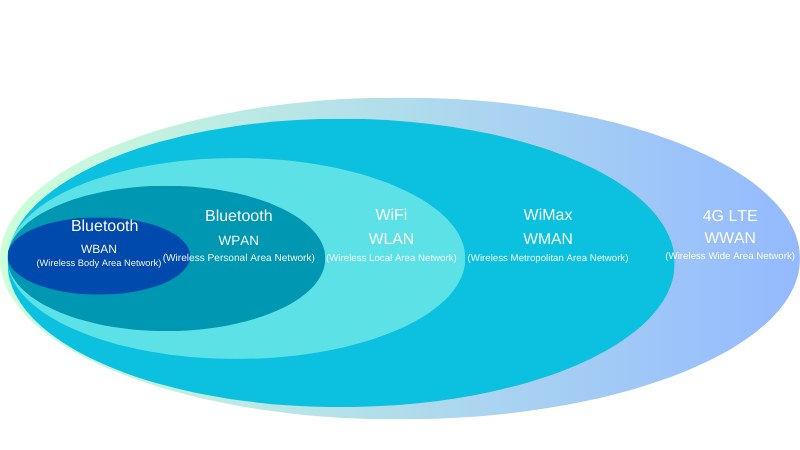
Comparison of Different Wireless Networks: WBAN, WPAN, WLAN, WMAN & WWAN
| Network Type | Full Name | Range | Description | Applications | Technology |
| WBAN | Wireless Body Area Network | Up to 2 meters | A communication network consisting of various network elements centered on the human body and within a 2-meter range around the body | WBAN is mainly used in healthcare systems | Bluetooth, Zigbee, Wi-Fi |
| WPAN | Wireless Personal Area Network | Up to 10 meters | Connects personal devices within a concise range, typically within a room. | Bluetooth connections, wireless keyboards, and headsets | Bluetooth, Zigbee, NFC |
| WLAN | Wireless Local Area Network | Up to 100 meters | It covers a small area, such as a home, office, or campus, and connects devices wirelessly within that space. | Home or office Wi-Fi networks, campus networks | Wi-Fi, Wi-Fi 6 |
| WMAN | Wireless Metropolitan Area Network | Up to 50km | A locally distributed wireless network for transmitting information between distributed nodes geographically covering a city and its suburban areas. | The internet, corporate networks connecting multiple cities or countries | MMDS、LMDS, WiMAX |
| WWAN | Wireless Wide Area Network | Worldwide | A type of WAN that uses wireless technologies to cover vast areas, connecting devices or networks across cities, regions, or globally. | Mobile networks, remote monitoring, global IoT networks | 4G LTE, 5G, satellite communication |
FAQ
Q: What can I do if my computer cannot read the SIM card?
A: You can first try to reinstall the SIM card. Please check if it is damaged and still cannot be read.
Q: Are WWAN network speeds stable?
A: WWAN network speeds are affected by various factors, such as signal strength and network congestion. When the signal is good and there are few users, the network speed is relatively stable and can meet the needs of most daily applications, such as browsing the web, sending and receiving emails, etc. However, when the signal is weak, or there is a high density of users, the network speed is relatively stable. However, the network speed may fluctuate or even slow down in areas with weak signals or dense users.
Q: What will the new development direction of WWAN technology be?
A: In the future, WWAN technology will develop towards higher transmission rates, lower latency, more significant connection density, and better network reliability. At the same time, WWAN technology will be deeply integrated with artificial intelligence, cloud computing, and other technologies to realize more intelligent and efficient network management and services. Connect environments such as smart cities and advanced IoT ecosystems will become commonplace.
Q: What are the applications of Wireless WAN?
Wireless Wide Area Network (WWAN) is a technology that provides long-distance wireless network connectivity, allowing users to access the Internet and other network services over a wide area. Here are some of the major application areas of wireless WAN:
- Mobile communications: e.g., voice calls, text messaging, and Internet access.
- Smart device connectivity: can be used to connect IoT devices, such as smart home devices, studios, vehicles, etc., at the network’s edge.
- Environmental monitoring: The wireless WAN can transmit Environmental information(such as monitoring air quality, water quality, and atmospheric conditions)to the server in real-time, making it easy for staff to view.
- Industry applications: For example, wireless bridge equipment is used in the tax system to realize wireless networking of each tax point, tax department, and tax bureau to improve office efficiency.
Conclusion
WWAN, a Wireless WAN technology, is expected to play a more significant role in emerging new areas such as the Internet of Things (IoT) and intelligent transportation. This article will help you understand WWAN clearly. Please let us know if you see any mistakes in the article so we can fix them.
Although WWAN has some limitations, its benefits will grow as technology advances. These developments will better support our mobile lives and help industries go digital. WWAN will drive global digitization and create a more convenient, efficient, and intelligent mobile network experience for everyone.
Read more
- Internet vs WiFi: What Are the Key Differences?
- WiFi 6 vs WiFi 7 vs WiFi 6E: What is the difference?
- 5G Front-Haul Networks and Optical Transceiver: What You Need to Know
Reference
- https://www.techtarget.com/searchnetworking/tip/As-wireless-WAN-matures-benefits-and-challenges-emerge
- https://www.minitool.com/lib/wwan.html