Network Cabling
What are Ethernet Crossover Cables?
We all know you need Ethernet cables to connect your computer to Ethernet via a wired connection. But how to choose the suitable cable correctly? Straight-through and crossover cables are Ethernet cables, so what is the difference between them? What kind of cable do you need to choose to connect two computers to each other?
In this article, we will discuss an Ethernet crossover cable, how to make one, and the differences between it and a straight cable.
Table of contents
What is A Crossover Ethernet cable?
An Ethernet crossover cable is a type of crossover cable for Ethernet that connects Ethernet network devices directly together. It is most commonly used to connect two devices of the same kind, such as two computers. Crossover cables are similar to straight-through cables, except that crossover cables have crisscrossing pairs of wires.
Crossover Cable vs. Straight-Through Cable: What is the Difference?
#1. Application Scenario
People often use Ethernet crossover cables to connect the same network equipment, such as computers connecting computers.

People often use straight-through cables to connect different types of network equipment, such as switches connected to routers and computers connected to switches.

#2. Wiring Standards
As we all know, T568A and T568B are Ethernet cable wiring standards recognized by ANSI, TIA, and EIA. They differ in the order of the 8 core colors, as shown in the figure below.

For T568A, the color sequence of the 8 pins is as follows: green white-l, green-2, orange white-3, blue-4, blue white-5, orange-6, brown white-7, brown-8. For T568B, the color sequence of the 8 pins is as follows: orange white-1, orange-2, green white-3, blue-4, blue white-5, green-6, brown white-7,brown-8, and compared with T568A, 1 pin for 3 pins, 2 pins for 6 pins.
Ethernet crossover cables use different wiring standards at both ends (connector A and connector B), T568A at one end, and T568B at the other, as shown in the following figure.

Ethernet straight-through cables use the same wiring standard at both ends (connector A and B), T568A or T568B. In practice, most applications use the T568B standard at both ends, which is generally considered better shielded against electromagnetic interference, as shown in the following figure.

#3. Appearance Difference
Ethernet crossover cables are printed with the word Crossover or Xover to distinguish them from straight-through cables. Or we can look at the RJ-45 header to see if the wire sequence is the same to differentiate.
-
 Cat8 Snagless Shielded (SFTP) 25G/40GBase-T Ethernet Network Patch Cable, PVC, BlackPrice range: US$ 2.25 through US$ 28.80 (Excl. VAT)
Cat8 Snagless Shielded (SFTP) 25G/40GBase-T Ethernet Network Patch Cable, PVC, BlackPrice range: US$ 2.25 through US$ 28.80 (Excl. VAT) -
 Cat6 Ethernet Network Patch Cable, Snagless Unshielded (UTP), PVC, BluePrice range: US$ 0.85 through US$ 13.10 (Excl. VAT)
Cat6 Ethernet Network Patch Cable, Snagless Unshielded (UTP), PVC, BluePrice range: US$ 0.85 through US$ 13.10 (Excl. VAT)
How to Make An Ethernet Crossover Cable?
Step 1
Strip approximately 1.5 cm of cable shielding from both ends. The crimping tool has a round area to complete this task.
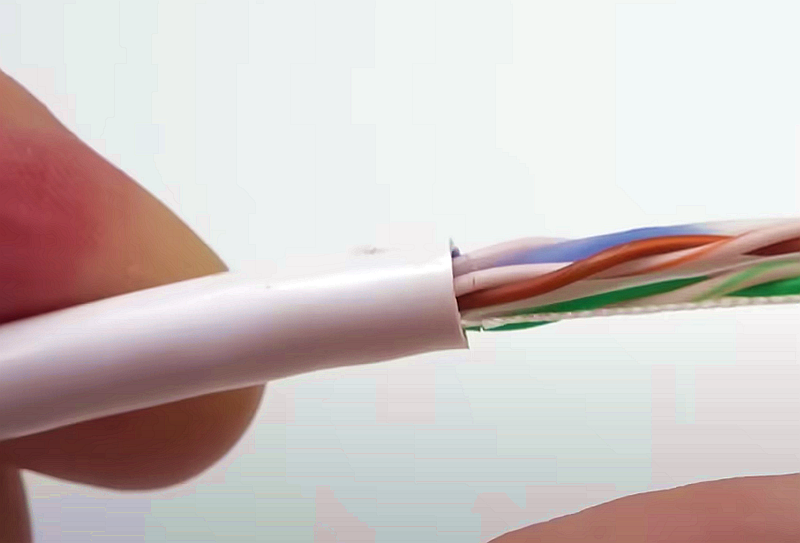
Step 2
After that, you will need to unravel the wires, which consist of four pairs of “twisted pairs.” Straighten them out and arrange them according to the wiring standards. One end should be arranged according to T568A, and the other according to T568B.

Step 3
If some wires stick out farther than others, cut them flat to create an even level. The problem is getting them into the RJ45 plug without messing up the order. Hold the plug so the clip side is back to you and the gold pin faces you.
Next, push the cable straight in. The copper core at the cable’s end will be next to the RJ45 header. If not, it means you stripped too much of the shield. Cut the cable a little further. Once the cable is firmly inserted into the plug, insert it into the crimping tool and push it down. Be careful, as too much force can crack the fragile plastic plugs.
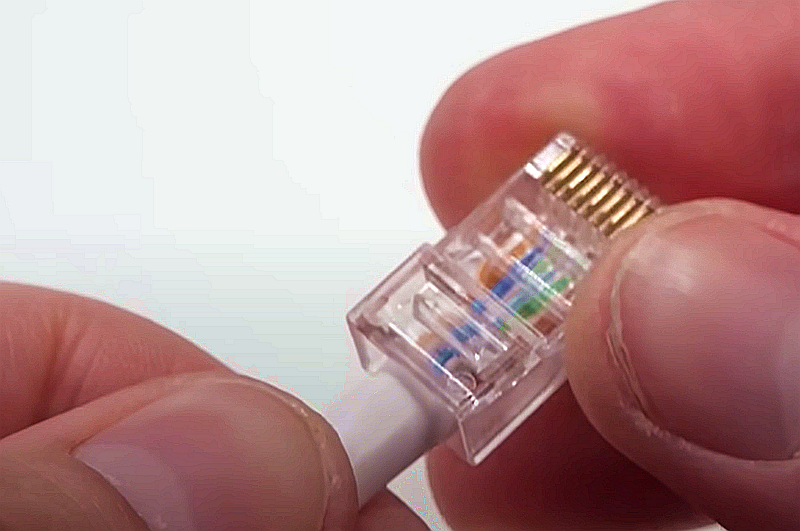
step 4
When both ends of the cable are made according to the above steps, a professional test tool is used to determine whether the making is successful.

Conclusion
The similarities between crossover cables and straight-through cables are apparent. Both Ethernet cables and crossover cables conform to the T568A and T568B cabling standards, and each side of the connector has eight different colored pins. The former connects two different types of devices, such as a computer, to switch, while the latter connects two devices of the same kind, one computer to another.
Read more
- Cat5, Cat5e, Cat6, Cat6a, Cat7, Cat7a vs Cat8 Ethernet Cable, What is the difference?
- Will PoE over Cat6 cable slow down network speed?
- Optics Options for HPE FlexFabric 5700 Switch Series
Reference







