Blog, Networking Device
PPPoE vs DHCP: What are the Differences, How to choose?
Updated: December 2, 2024
Connecting to the Internet requires two different protocols: PPPoE vs DHCP. The PPPoE network protocol is usually used to connect to an ISP through the PPP protocol, and DHCP dynamically assigns IP addresses to clients. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each?
In this article, you will learn more about the differences between DHCP vs PPPoE and understand their role in your network system.
Table of contents
What is PPPoE?
PPPoE is a network protocol whose full name is Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet. It encapsulates the Point-to-Point Protocol, or PPP, within an Ethernet frame. The protocol provides secure and reliable Internet connectivity for areas where the primary connection is a subscriber line (DSL) or cable system.
The outstanding advantage of PPPoE is that it provides authentication to the user, ensuring Internet access security.
The typical PPPoE architecture consists of a client, a server, a host computer, and an ADSL modem, as shown in the figure below.

What is DHCP?
DHCP is also a network protocol. Its full name is Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol. The word dynamic visualizes DHCP’s advantages: IP addresses and other related configurations can be dynamically assigned to network devices. This eliminates the need for network administrators to configure IP addresses for new computers manually.
Typically, the DHCP architecture consists of a DHCP client, a DHCP server, and a DHCP relay agent (usually a router or switch with DHCP), as shown in the following figure:

DHCP vs. Static IP
DHCP dynamically assigns IP addresses, which can significantly reduce the administrative overhead of managing many network devices. It also makes it easy to quickly expand a network in environments where devices frequently join and leave. DHCP is beneficial for organizations that use mobile devices or guest Wi-Fi networks.
Static IP is the opposite of dynamic IP, which remains consistent and unchanged. It is essential for network infrastructure, such as printers and servers. A small local area network with a fixed static IP significantly avoids the hassle of IP address conflicts. Because the IP address is fixed, it is easy for administrators to anticipate and solve problems if they arise in the network.
How does PPPoE work?
The PPPoE workflow can be divided into discovery, session, and termination.

Discovery phase
As shown in the figure above, the Discovery phase consists of four steps, and its basic workflow is described below.
- PADI: First, the PPPoE client has to send a PADI (PPPoE Active Discovery Initiation) packet by broadcasting, which includes the type of service requested by the client.
- PADO: When the PPPoE server (BRAS) receives a PADI packet, it determines whether it can provide the service. It sends a PADO (PPPoE Active Discovery Offer) packet to the client if it can. If the PPPoE server cannot provide service for PADI, it is not allowed to respond with PADO packets.
- PADR: Since PADI is sent out as a broadcast, the PPPoE client may receive more than one PADO packet. It will review all the received PADO packets, select a PPPoE server based on the server name or services provided, and send a PADR (PPPoE Active Discovery Request) packet to the selected server. The PADR packet includes the services requested by the client.
- PADS: When the PPPoE Server receives the PADR packet from the client, the PPPoE Server generates a unique session identifier to identify this PPPoE session between it and the PPPoE Client. and responds to the PPPoE Client by including this specific session identifier in the session confirmation message PADS (PPPoE Active Discovery Session-confirmation), and proceeds to the PPP session phase if no error occurs, and the PPPoE Client, upon receives the session acknowledgment message also enters the PPP session phase if no error occurs.
When the discovery phase usually ends, both parties stop communicating to obtain the session identification (Session ID) and the other party’s MAC address.
Session Phase
The PPPoE Discovery phase establishes a Session between the PPPoE Client and the PPPoE, after which the PPPoE enters the Session phase. The Session phase can be divided into the PPP negotiation phase and the PPP message transmission phase. The PPP negotiation on the PPPoE Session is the same as the standard PPP negotiation and is divided into three phases: LCP negotiation, authentication, and NCP negotiation. So, The PPP session phase includes LCP negotiation, PAP/CHAP authentication, NCP negotiation, and other phases.
LCP negotiation
After entering the PPP session phase, LCP negotiation is performed first.
PAP/CHAP authentication
After the LCP negotiation, the authentication phase, which supports both PAP and CHAP authentication, is entered.
PAP is a two-handshake protocol that authenticates the user through the user name and password and transmits them in clear text. The PPPoE Server (or RADIUS server) checks whether the user name and password are correct according to the user table on the local side.
CHAP is a three-time handshake protocol used by the PPPoE Server (or RADIUS server) according to the local user table to check whether the user name and password are correct. However, the CHAP authentication method transmits only the user name over the network, not the user password, which is more secure than PAP.
NCP Negotiation
NCP negotiation is similar to the LCP process. Its primary function is to negotiate the network layer parameters of PPP messages, such as IPCP, IPv6CP, etc. The PPPoE Client mainly obtains the IP address or IP address segment to access the network through the IPCP protocol.
After a successful NCP negotiation, the PPPoE Client goes online. The PPPoE Server (usually a BRAS device) sends a billing request message to the RADIUS server to bill the PPPoE Client through the RADIUS server.
Terminate Phase
The PPP communicating parties should use the PPP protocol itself (such as the PPP Terminate message) to end the PPPoE session, but you can use the PADT message when you cannot use the PPP protocol.
How does DHCP work?
The DHCP works slightly differently depending on whether the client logs on to the network for the first time. Here, we will focus on the four processes of a new client lease.
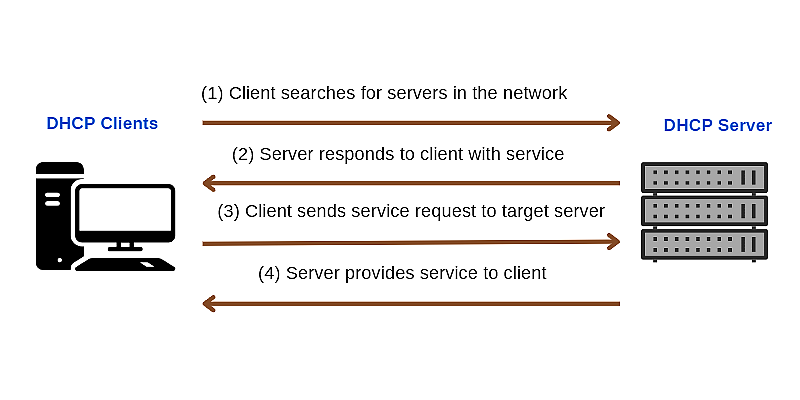
Dynamic IP address acquisition process operates through a four-step process called DORA (Discover, Offer, Request, Acknowledge):
- Discovery Phase: This is the process by which a DHCP client looks for a DHCP server. When the device connects to the network, it broadcasts a DHCP discover message to identify any available DHCP servers.
- Offer phase: the phase in which the DHCP server provides an IP address. The DHCP server responds to a DHCP discover message by selecting one of the pool of unassigned IP addresses to assign to the DHCP client and then sends a DHCP offer provisioning message to the DHCP client that contains the assigned IP address and other settings.
- Request phase: the phase in which the DHCP client selects an IP address offered by a DHCP server: if more than one DHCP server sends offer messages to the client, the client accepts only the first DHCP offer message it receives, and at the same time the DHCP client broadcasts and sends out a DHCP Request message containing the IP address it selected for the DHCP The DHCP client will broadcast a DHCP Request message containing the IP address of the DHCP server it has chosen.
- Acknowledgment phase: the phase in which the DHCP server confirms the IP address. When the DHCP server receives a DHCP Request message, it sends a DHCP ack message to the DHCP client. This message confirms the leased IP address and other configuration details. The client is told to use this IP address, and then the client binds the TCP/IP protocol to the network card.
DHCP vs PPPoE: What is the Difference
Function
PPPoE is mainly used to establish a reliable point-to-point connection between client devices and ISPs, providing dial-up Internet access, user authentication, and bandwidth control. On the other hand, DHCP is mainly used to assign IP addresses and other network configuration information automatically.
Cost
PPPoE may involve additional costs, such as purchasing and installing PPPoE client software, whereas DHCP is usually included as part of the network infrastructure. DHCP is more cost-effective in this regard.
Security
DHCP vs PPPoE: PPPoE has advantages over DHCP in terms of security. PPPoE requires a username and password for user authentication, which increases security and access control. DHCP Simplifies connectivity by eliminating the need for authentication. Therefore, in environments where high security is required, the PPPoE protocol may be more appropriate for your network.
IP Address Assignment
PPPoE: Static or dynamic IPs can be assigned. And unless a static IP is configured, the address may change with each session. DHCP: DHCP can assign IP addresses through three main mechanisms: automatic, dynamic, and manual. Each option meets different network requirements and policies. The most common is assigning dynamic IPs, which effectively manage IP addresses in environments where devices are frequently connected and disconnected from the network.
Performance overhead:
PPPoE: Performance overhead due to session management and encapsulation, which can affect high-traffic environments. DHCP has lower overhead due to no session management or encapsulation, making it more efficient for high-traffic networks.
Configuration complexity
DHCP vs PPPoE: DHCP is more complex to manage and configure than PPPoE, which requires complex setup, authentication, and session management. However, it is also easier to troubleshoot and personalize network access control. DHCP is more straightforward to configure and manage, requiring minimal setup to handle IP address assignment automatically. It reduces manual configuration effort and improves network management efficiency.
Network Control
PPPoE enables network administrators to control and allocate bandwidth to each user. In contrast, DHCP does not provide this level of control.
| PPPoE | DHCP | |
| Architecture | PPPoE client, PPPoE hosts, PPPoE modems and hosts are all included in this group. | It comprises a DHCP client, DHCP server, and DHCP relay agent(usually a router/switch with DHCP). |
| IP Assignment | Randomly assigns lP addresses to users from all available lP addresses. | A unique lP address is assigned to a user. |
| Require Dial-up Client | Yes | No |
| Authenticate Access | Yes | No |
| Security | High | Low |
| Configuration Difficulty | Complex | Simple |
| Purpose | Able to set up P2P connection over Ethernet | Assign an IP address for access |
PPPoE vs. DHCP: Different Usage Scenarios
Both the DHCP and PPPoE protocols have their unique features and environments. The following are typical usage scenarios for each protocol:
The PPPoE protocol is primarily used in user authentication, billing, and bandwidth control scenarios. This is common in DSL or fiber optic broadband setups. For example, in a school dormitory, a student’s network may need to be billed separately and require authentication to access different levels of broadband service.
DHCP is used when IP addresses and other network configuration information must be automatically assigned to many devices. For example, in an organization where many devices need to be connected, mobile devices frequently connect and disconnect from the network. In this case, using PPPoE requires manually configuring IP addresses, which can be cumbersome. By using the DHCP protocol, network administrators can automatically assign network configuration information to each device without having to configure it manually, thus improving network management efficiency.
PPPoE vs DHCP: What’s the Choice?
If you need a secure network access environment, PPPoE can provide an authentication mechanism for network security, especially in a broadband environment. However, if you care about the security and manageability of your network, PPPoE may be more suitable for you.
If you are using a cable modem or fiber optic connection, you should use DHCP. Most cable modems and fiber optic routers support DHCP, which is the easiest way to configure. DHCP is suitable for dynamic IP address assignment without configuring additional authentication and for general homes and small networks. Therefore, if you need a simple and easy-to-use connection, you can choose DHCP;
However, if you use a DSL connection, you may need to use PPPoE. Not all DSL modems support DHCP, so you may need to obtain PPPoE credentials from your ISP.
Finally, If you are unsure whether to use DHCP vs PPPoE, contact your ISP. ISPs usually specify the protocol they want their customers to use to connect to the Internet. They can help you determine which option is best for your connection type.
FAQ
Q. IPoE vs PPPoE: what is the Difference?
A. The differences are shown in the table below:
| Item | PPPoE | IPoE |
| Full Name | Point-to-Point Protocol over Ethernet | Internet Protocol over Ethernet |
| Connection | PPPoE is a connection-oriented protocol. Session establishment is done before this protocol is used | IPoE is a connectionless protocol |
| Multicast Traffic | PPPoE does not support Multicast traffic efficiently | IP Over Ethernet is a good solution for multicast traffic |
| Authentication | PPPoE requires user authentication | IPoE does not need authentication |
| Authentication Efficiency | low | high |
| Address assign | IPCP, based on user name and password | DHCP, based on line information and MAC |
| Anti-spoofing | high(unique session ID) | high(anti-spoofing policy) |
Q. How do I find my DHCP address?
A. First, use the Win+R key, type cmd to enter the command prompt window, then type Ipconfig. Finally, find your network adapter or “WIFI adapter,” and check the IPV4 or IPv6 address, which is your DHCP address.
Q. How can I find my PPPoE address?
A. To find your PPPoE IP address, you should check the status section of your router or modem configuration screen. Most routers have a web-based interface where you can log in and view the status of your network connection, including PPPoE sessions. The PPPoE IP address and other connection details, such as status, duration, and data usage, are usually displayed.
Q. How does a DHCP client connect to the network using DHCP?
A. A DHCP client uses the DHCP protocol to send requests to a DHCP server on the network. The client requests an IP address and other configuration information, and the DHCP server responds with an assigned IP address and lease term.
Q. What role does the PPPoE server play in the connection process?
A. PPPoE servers handle authentication and session management for PPPoE connections. They validate the credentials of the client device, establish the session, and manage the data transfer between the client and the server.
Q. Why use PPPoE instead of IP directly?
A. PPPoE is a Layer 2 connectivity protocol. IP is a Layer 3 protocol requiring a Layer 2 connection. Without Layer 2 connectivity, Layer 3 protocols are useless.
Q. Should I set my home router to use DHCP or static IP?
A. It doesn’t hurt to use either one. However, DHCP is flexible and will save you time by allowing you to update the IP addresses of new systems you add to your network automatically.
Q. What is the difference between PoE and ADSL?
A. ADSL is a digital subscriber line technology that transmits digital data over ordinary telephone lines. PPPoE is a protocol that establishes a point-to-point connection between a LAN and a broadband access point. In short, they are often used together, and users will authenticate and establish a connection through the PPPoE protocol when using the ADSL service.
Conclusion
This article has explained DHCP vs. PPPoE in several dimensions so you may have some theoretical knowledge. However, you may still find them vague and difficult to understand. Finally, I will give a simple example to help you know.
Using the PPPoE protocol, broadband access personnel come to the user’s home to install broadband. They set up a user and password for the customer to confirm that the user is a legitimate user of the ISP (paid the network fee). Then, you can use ISP dial-up to obtain a valid IP address.
As long as the user’s home through the ISP to obtain a legitimate Internet address, in the user’s own house in the small LAN is through the router (DHCP server) for IP allocation again (that is, the allocation of host names), so that a user’s home to meet the needs of multiple terminals on the Internet.
To learn more about networking, fiber optic patch cords, or optical transceivers, check out our blog or call OPTCORE‘s technical staff!
Reference
- https://info.support.huawei.com/info-finder/encyclopedia/zh/PPPoE.html







