Blog, Optical Networking
Baud Rate vs Bit Rate: What is the difference?
Transmission speed is a key metric in communication systems, and transmission rates are critical to their efficiency, accuracy, and performance. Baud rate and bit rate are important concepts in communication systems. This article will provide a beginner’s guide to the baud rate vs bit rate and explain their differences.
What is the Baud Rate?
“Baud” is abbreviated to ‘Bd’, referring to Émile Baudot, who invented the Baudot code in the 1870’s. Baud rate is measured in Baud rate (Bd). The baud rate is the rate at which information is transmitted over a communications channel and is used to indicate the number of signaling events (i.e., symbols) that pass through the transmission medium each second.
A higher baud rate means faster information transmission and reception between communication devices. In addition, the baud rate determines the transmission bandwidth of the communication channel and the bit rate calculation.
Baud rate is commonly used to discuss electronic devices that use serial communication. In the context of a serial port, “9600 baud” means that the serial port can transmit up to 9600 bits per second. At baud rates higher than 76,800, shorter cable lengths are required. The higher the baud rate, the more sensitive the cable is to the quality of the installation because of how many wires are unraveled around each device!
What is the Bit Rate?
Bit rate is the number of bits transmitted or processed per unit of time. Bitrate is expressed in units of bits per second (bit/s).
It is often used in conjunction with International System of Units prefixes such as kilo (1 kbit/s = 1,000 bit/s), megabyte (1 Mbit/s = 1,000 kbit/s), gigabyte (1 Gbit/s = 1,000 Mbit/s), or trillion (1 Tbit/s = 1,000 Gbit/s). The non-standard abbreviation bps is often used in place of the standard notation bit/s; for example, 1 Mbps is used to denote 1 million bits per second.
Baud Rate vs Bit Rate
#1: The Relationship Between Baud Rate And Bit Rate
The relationship between baud rate and bit rate can be expressed as follows:
Bit Rate = Baud Rate × Bits per Symbol
Regarding the number of bits per symbol, we must mention the modulation technique used in communication systems. Modulation is the encoding of digital information into an analog signal for transmission. Different modulation techniques can transmit different amounts of information per signal change or symbol.
For example, in binary Amplitude Shift Keying (ASK) and Frequency Shift Keying (FSK), one bit of information is transmitted for each signal change, so the baud rate equals the bit rate.
However, transmitting multiple bits with a single signal change is possible in more advanced modulation techniques, such as Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (QAM) or Phase Shift Keying (PSK). For example, in 16-QAM, each symbol represents 4 bits of information. In this case, the bit rate is four times the baud rate.
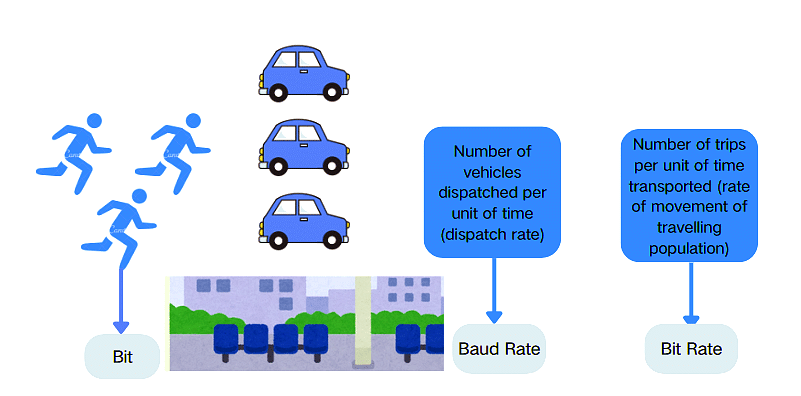
Let’s take a life example to deepen our understanding of these two concepts. A communication system is similar to our public transportation system. We can analogize the code elements in a communication system to public vehicles, such as buses, subways, cabs, and so on.
Currently, the number of bits transmitted by the communication system is analogous to the number of people traveling. The bit rate is the travel speed of the population flow, and the baud rate is the departure rate.
#2: The Comparision Between Baud Rate And Bit Rate
| Baud rate | Bit rate | |
| Definition | The Baud rate refers to the total number of signal units transmitted in one second. | The Bit rate refers to the total Bits transmitted in one unit of time. |
| Formula | Bit rate = Baud rate x bits per signal or symbol or Bit rate = number of bits transmitted/ total time (in seconds) | Baud rate = number of signal elements/total time (in seconds) |
| Generally Used | It mainly concerns the transmission of data over a given channel. | It mainly focuses on the efficiency of a computer. |
| Significance | A high baud rate typically means your system can process more information from multiple users | A high bit rate means that the system can process that information quickly |
| bandwidth | It is not required to decide the bandwidth for the signal transmission. | The baud rate is required in bandwidth for signal transmission |
Conclusion
Do you have a general understanding of the baud rate and bit rate through this article?
This article explains the baud rate and bit rate, which are key indicators of transmission speed in a communication system. The relationship between the two is that the bit rate equals the baud rate multiplied by the number of bits per symbol. The number of bits in a symbol varies depending on the technology, so the baud rate and bit rate are not always equal.
Maybe there are some errors in the article. Feel free to discuss with me in the comment section.
FAQ
Q. What is the main difference between bit rate and baud rate?
A. Bit rate measures the number of bits per second, while baud rate measures the signal changes per second.
Q. Can the baud rate be higher than the bit rate?
A. No, because the Baud Rate can correspond to multiple bit changes in a signal, the Bit Rate is equal to or greater than the Baud Rate.
Q. What is the relationship between Bit Rate and Bandwidth?
A. Higher bit rates require more bandwidth to transmit data efficiently.
Q. Why is bit rate important?
A. It determines the speed of transmission, which affects the general efficiency of a communication system.
Q. How does bit rate affect video quality?
A. Higher bit rates result in higher video quality, while lower bit rates result in lower quality.
Read more
- What Is Plenum Cable? OFNP Cable Explained
- Understanding SNAP12: What You Need to Know
- Internet vs WiFi: What Are the Key Differences?
- What is ONT? Everything You Need to Know
- LC vs SC vs MU Connectors: What is the Difference?
Reference
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-btween-bit-rate-and-baud-rate/?ref=oin_asr1
- https://www.wevolver.com/article/baud-rates







