-
×
 10Gb/s CWDM XFP ER 1470~1610nm 40km Transceiver
1 × US$ 379.00
10Gb/s CWDM XFP ER 1470~1610nm 40km Transceiver
1 × US$ 379.00
Optical Networking, Optical Transceiver
CWDM Wavelength ITU Channels List: A Complete Guide (2022)
We explored the DWDM wavelength channel issue in the previous day’s article. As a series of articles, we are back to discussing CWDM Wavelength Channel issues today.
This article is a complete guide to Corse Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (CWDM) Wavelength in 2022.
Therefore, if you would like to.
- Understand what CWDM Wavelength-Division Multiplexing technology is
- Understand the CWDM Wavelength Channels List
- How to choose the suitable CWDM transceiver optics
Then you will enjoy this new guide.
Let’s get started.
Table of Contents
- What is Edge Computing?
- Types of Edge Computing
- Advantages of Edge Computing
- Disadvantages of Edge Computing
- Conclusion
Coarse Wavelength-Division Multiplexing (CWDM) Basics
CWDM is a widespread WDM technology. It refers to sparse wavelength division multiplexing. Unlike dense WDM, CWDM has a channel spacing of 20nm and can support up to 18 wavelengths. The ITU-T G.694.2 recommendation specifies a wavelength range of 1271 nm to 1611 nm for use in CWDM.
The below figure shows the typical CWDM system.
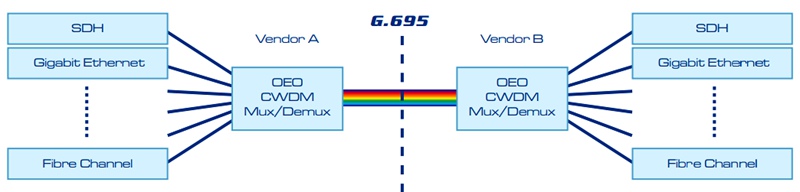
Compared to DWDM, the wide channel spacing of CWDM allows cheaper CWDM network components such as uncooled lasers or lower-quality multiplexers and multiplexers. However, this broad spectral range hinders the use of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers. Because erbium-doped fiber amplifiers work best around 1550 nm, this limits the maximum capacity for CWDM deployments to about 60 or 80 km.
Because CWDM systems have a relatively low overall cost and can support up to 18 channels, this makes CWDM an attractive choice for metro networks requiring additional bandwidth and lower price. But for longer transmission distances and the need for more extensive bandwidth channel backbone networks, DWDM systems are suitable.
CWDM Wavelength ITU Channels List
ITU-T recommends 16 wavelength channels for CWDM systems in the G.694.2 Standard. CWDM wavelength grid is shown in the below CWDM Wavelength Channels Chart.
As you can see from the CWDM Wavelength Channels Chart, each CWDM channel has a 20nm spacing and falls within the 1271 nm to 1611 nm wavelength.
The most commonly used wavelength is 1471nm to 1611nm, covering most of the CWDM application scenarios. While for extended wavelength capacity, you may also choose 1271nm to 1451nm, which provides additional 10 wavelength channels.
| No. | Wavelength (nm) | Wavelength Band |
| 1 | 1271nm | O-Band |
| 2 | 1291nm | O-Band |
| 3 | 1311nm | O-Band |
| 4 | 1331nm | O-Band |
| 5 | 1351nm | O-Band |
| 6 | 1371nm | E-Band |
| 7 | 1391nm | E-Band |
| 8 | 1411nm | E-Band |
| 9 | 1431nm | E-Band |
| 10 | 1451nm | E-Band |
| 11 | 1471nm | S-Band |
| 12 | 1491nm | S-Band |
| 13 | 1511nm | S-Band |
| 14 | 1531nm | C-Band |
| 15 | 1551nm | C-Band |
| 16 | 1571nm | L-Band |
| 17 | 1591nm | L-Band |
| 18 | 1611nm | L-Band |
FAQs about Coarse Wavelength Division Multiplexing (CWDM)
Q: How many wavelength channels can CWDM support?
A: CWDM can support up to 18 wavelength channels.
Q: What is CWDM’s typical channel spacing?
A: CWDM has a channel spacing of 20nm.
Q: What is the CWDM wavelength range?
A: The CWDM wavelength range is 1271 nm to 1611 nm.
Q: What are the advantages of CWDM vs. DWDM?
A: CWDM has a lower overall cost and can support up to 18 channels. However, the broad spectral range hinders the use of erbium-doped fiber amplifiers.
DWDM has a narrower spectral range but can support up to 80 or 160 channels. This enables DWDM to transmit data over longer distances and at higher bandwidths. However, DWDM systems are significantly more expensive.
Q: What optical components are required for a complete CWDM system?
A: CWDM systems require CWDM Mux/Demux, CWDM transceiver modules, and fiber cables.
Q: CWDM vs. DWDM Transceiver, What is the difference?
A: CWDM transceiver features a CWDM transmitter for use in the CWDM system, while the DWDM transceiver has a DWDM transmitter for use in the DWDM system. Moreover, the CWDM transceiver is usually priced lower than the DWDM transceiver.
Optcore CWDM Transceiver Solution
Optcore CWDM transceivers are designed for CWDM networks. They offer a wide passband that supports multiple CWDM wavelength channels and are available in 1×9, SFP, XFP, SFP+, and SFP28 form factors. Optcore CWDM transceivers are highly reliable and pass the performance test to meet the requirements of CWDM networks.
The below table shows the detailed CWDM transceiver and supported platform.
| Part # | Product Description | Data Rate | Wavelength | Distance | Support Platform (Compatibility) |
| OPC10G-xx40DCR | CWDM SFP+ ER | 10Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 40km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Brocade |
| OPC10G-xx80DCR | CWDM SFP+ ZR | 10Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 80km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Brocade |
| OXC10G-xx40DCR | CWDM XFP ER | 10Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 40km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Brocade |
| OXC10G-xx80DCR | CWDM XFP ZR | 10Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 80km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Brocade |
| OPC1250-xx80DCR | CWDM SFP ZX | 1Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 80km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Brocade |
| OPC1250-xxA2DCR | CWDM SFP EZX | 1Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 120km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Brocade |
| OPC2488-xx80DCR | SDH CWDM SFP ZX | 2.5Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 80km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Nokia |
| OPC2488-xxA2DCR | SDH CWDM SFP EZX | 2.5Gbps | 1470-1610nm | 120km | Compatible with Cisco, HPE, Juniper, Arista, Nokia |
-
 Optcore 1.25G CWDM SFP 1270~1610nm 80km TransceiverUS$ 35.00 (Excl. VAT)
Optcore 1.25G CWDM SFP 1270~1610nm 80km TransceiverUS$ 35.00 (Excl. VAT) -
 Optcore 2.5G CWDM SFP 1270~1610nm 80km TransceiverUS$ 44.00 (Excl. VAT)
Optcore 2.5G CWDM SFP 1270~1610nm 80km TransceiverUS$ 44.00 (Excl. VAT) -
 Optcore Generic Compatible 10G CWDM SFP+ ER 1470~1610nm 40km TransceiverUS$ 139.00 (Excl. VAT)
Optcore Generic Compatible 10G CWDM SFP+ ER 1470~1610nm 40km TransceiverUS$ 139.00 (Excl. VAT) -
 10Gb/s CWDM XFP ER 1470~1610nm 40km TransceiverUS$ 379.00 (Excl. VAT)
10Gb/s CWDM XFP ER 1470~1610nm 40km TransceiverUS$ 379.00 (Excl. VAT)
Final Words
That is the complete guide for CWDM Wavelength ITU Channels List in 2022. CWDM is a great technology that can offer many benefits for your network. We hope you found this guide helpful, and if you have any questions, please feel free to contact us.
Read more:
- DWDM Wavelength ITU Channels Chart: A Complete Guide (2022)
- OPTCORE Best 10G CWDM SFP+ Transceiver Solution
- Do You Know the CWDM Transceiver Color Code?